Key Differences Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Logistics Management
In today's globalized economy, the terms "Logistics" and "Supply Chain Management" (SCM) are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct concepts with their roles and responsibilities. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. This blog explores logistics and supply chain management's meaning, importance, and critical objectives. They also offer their key differences and clear guides for better understanding.
Major Differences Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
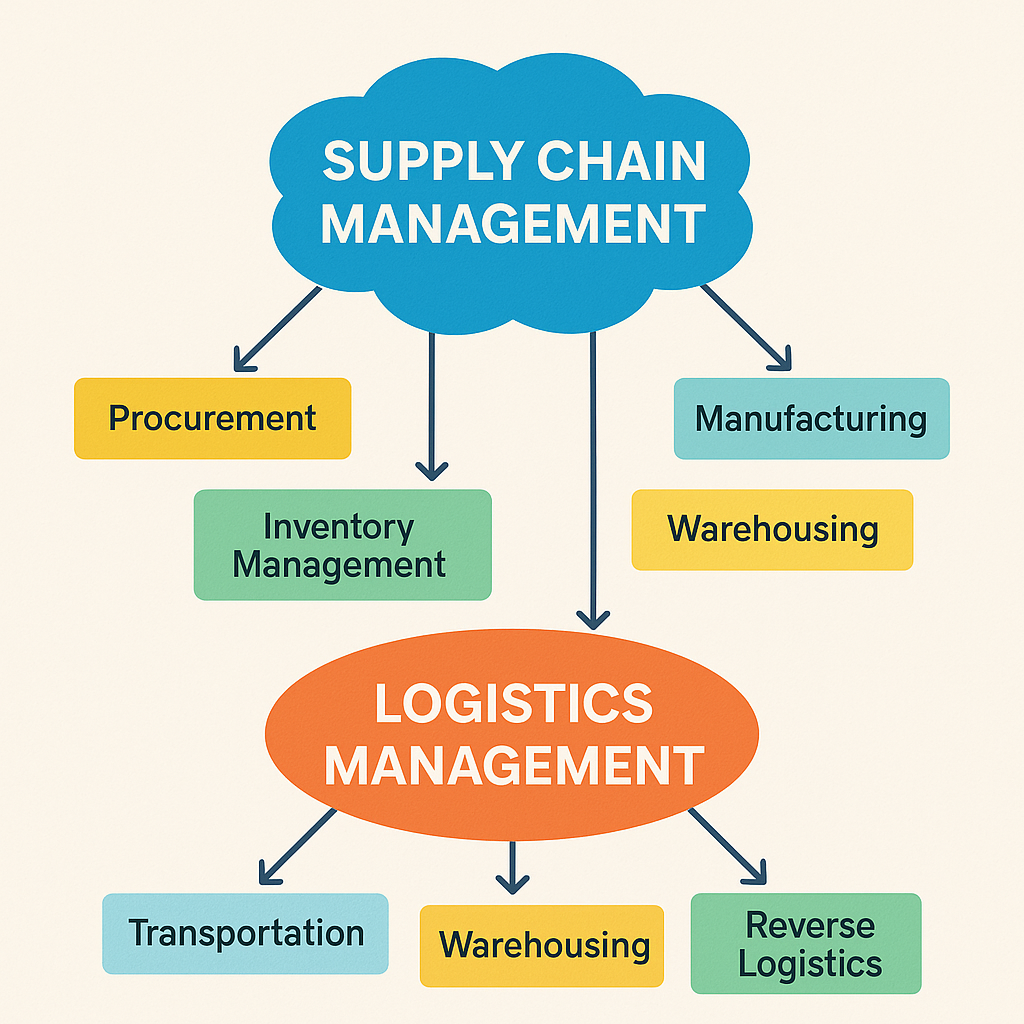
Understanding the difference between logistics and supply chain management is essential for anyone involved in business operations, transportation, or commerce. Although the terms are often used interchangeably, they serve different yet interconnected functions in a business.
What Is Logistics and Supply Chain Management?
Logistics and supply chain management are two critical components of business operations that deal with the flow of goods and services. While logistics management focuses on the efficient movement and storage of products, supply chain management (SCM) is a broader term encompassing every step from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product to consumers.
Logistics Management Meaning
Logistics refers to the detailed coordination of complex operations involving moving goods, services, and information from origin to consumption. It encompasses several activities: transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfilment, and distribution. The primary goal of logistics is to ensure that the right product reaches the right place at the right time, in the proper condition, and at the correct cost.
- Transportation logistics (moving goods)
- Warehouse logistics (storing goods)
- Reverse logistics (handling returns)
Logistics aims to ensure timely delivery, reduce transportation and storage costs, and streamline operations.
Supply Chain Management Meaning
Supply chain management covers the entire process of managing the flow of goods. It turns raw materials into final products and delivers finished goods to customers. It includes all activities in sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, and providing the final product to the end consumer. SCM integrates various procurement, production, logistics, and coordination processes with suppliers, intermediaries, third-party service providers, and customers.
- Procurement of raw materials
- Inventory management
- Manufacturing
- Warehousing
- Logistics
- Distribution to end customers
The term supply chain management was first coined in the early 1980s and has evolved to represent a strategic approach to managing the flow of goods, information, and finances across the entire supply chain.
Maximize your eCommerce efficiency with our latest guide on top sales channel integrations! Learn how to connect platforms like Shopify, Wix, WooCommerce, and Magento to the ILS Panel. Streamline your order management, improve delivery efficiency, and ensure a smooth customer experience.
What are Logistics and Supply Chain Management?
Logistics
Logistics refers to the detailed coordination of complex operations involving moving goods, services, and information from origin to consumption. It encompasses several activities: transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfilment, and distribution. The primary goal of logistics is to ensure that the right product reaches the right place at the right time, in the proper condition, and at the correct cost.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Supply chain management covers the entire process of managing the flow of goods. It turns raw materials into final products and delivers finished goods to customers' hands. It includes all activities in sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, and providing the final product to the end consumer. SCM integrates various procurement, production, logistics, and coordination processes with suppliers, intermediaries, third-party service providers, and customers.
What is the Key Difference Between Supply Chain Management and Logistics?
The key difference between logistics and supply chain management is overall coverage and where they focus.
NetSuite explains the important differences between supply chain management and logistics management, highlighting their unique roles in optimizing business operations.
-
Scope:
- Logistics: Focuses primarily on the efficient and effective movement and storage of goods within the supply chain. It deals with activities like transportation, warehousing, and inventory management.
- Supply Chain Management: Encompasses a broader range of processes, including logistics, procurement, production, and coordination with suppliers and customers. SCM aims at optimizing the entire supply chain from raw material acquisition to final delivery.
-
Focus:
- Logistics: Concentrates on managing goods flow and storage, ensuring that products are delivered to the correct location, time, and condition.
- Supply Chain Management: Focuses on the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain, aiming to create value, build a competitive infrastructure, and synchronize supply with demand.
Key Differences Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Here's a detailed comparison between the two:
| Feature | Logistics Management | Supply Chain Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on moving and storing goods | Covers end-to-end process from sourcing to delivery |
| Primary Objective | Optimize transportation, storage, and delivery | Enhance overall efficiency and customer satisfaction |
| Scope | Limited to movement and storage | Broad scope including procurement, manufacturing, etc. |
| Key Activities | Transportation, warehousing, inventory, returns | Planning, sourcing, production, logistics, return flows |
| Focus Area | Warehouses, carriers, distribution centers | Vendors, suppliers, logistics providers, manufacturers |
| Skills Required | Strong analytical and coordination skills | Analytical, communication, and negotiation skills |
| Professionals | Logistics coordinators, warehouse managers | Supply chain analysts, procurement managers |
Understanding the Major in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Logistics and Supply Chain Management helps students understand how to handle transportation, warehouse management, and inventory management. Students learn how to connect these areas to create a well-organized supply chain. The program covers planning supply chain strategy, purchasing materials, and using cutting-edge technology to keep everything running smoothly.
What is Logistics Management?
Guide, Definitions, and Importance of Logistics Management
Logistics management is the process of planning, executing, and managing the movement of goods and services, as well as reverse logistics. The logistics management is dedicated to delivering products to the right location, at the right time, and in the right condition.
Definitions:
- Importance: Logistics management is crucial for maintaining the flow of goods in a supply chain, reducing costs, improving delivery times, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Importance: Logistics management is crucial for maintaining the flow of goods in a supply chain, reducing costs, improving delivery times, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Importance of Logistics Management:
- Cost Efficiency: Companies can save money and improve their profits by improving transportation and warehousing.
- Customer Satisfaction: Efficient logistics plays a key role in improving customer satisfaction. It helps to deliver products on time, happy customers are more likely to stay loyal to the brand.
- Streamlined Inventory Management: Effective logistics management helps maintain the right amount of inventory and avoids having excess stock or stockouts.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with superior logistics management can offer better service levels, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Guide, Definitions, and Importance of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management involves the entire process of management of the flow of goods and services from one place to another. It covers everything from turning raw materials into finished goods. The main goal is to enhance a business's supply process better so that customers get more value for their money. Effective SCM helps companies stand out in the market and stay ahead of the competition.
Definitions:
- Supply Chain Management: The handling of the entire production flow of a good or service, from the raw components to the final product to the consumer.
- Importance: SCM is vital for creating value, reducing costs, and achieving a sustainable competitive advantage.
Importance of Supply Chain Management:
- Integration and Coordination: Supply Chain Management (SCM) integrates different steps and people involved in a product’s journey, ensuring everything works smoothly and improving overall efficiency.
- Cost Reduction: Supply Chain Management (SCM) simplifies how companies purchase, produce, and deliver products. By making these steps better businesses can save money and earn more profit.
- Quality Improvement: Supply Chain Management (SCM) focuses on making things better all the time. It helps companies keep their production and delivery at high standards. This means customers get the best products, leading to happier customers.
- Risk Management: Powerful supply chain management (SCM) identifies possible risks that impact the supply chain and implements strategies to reduce the risks. This ensures that businesses run smoothly without any problems.
Delve into the complex world of shipping and logistics with our latest blog post on the ILS Portal! The differences between shipping and logistics, explore various types of logistics and learn practical tips for optimizing your logistics operations. Whether you're a business owner or just curious about the subject, this comprehensive guide covers everything from inventory management to automated shipping solutions.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Whether looking into logistics and supply chain management jobs, planning a career move, or improving business operations, knowing how these functions differ and how they work together can drive better decision-making.
- Logistics and supply chain professionals must align goals and collaborate.
- SCM professionals often rely on logistics data to make strategic improvements.
- Logistics providers execute the transport and storage activities outlined in the supply chain plan.
Career Opportunities
With the growing complexity of global trade, the demand for experts in logistics & supply chain management is rising. Common roles include:
- Logistics Manager
- Supply Chain Analyst
- Warehouse Operations Manager
- Procurement Specialist
- Transportation Coordinator
These positions require strategic thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
Conclusion
While logistics and supply chain management are closely related, understanding their differences is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their operations. Logistics focuses on the efficient movement and storage of goods, while supply chain management encompasses a broader range of activities, including procurement, production, and coordination with suppliers and customers. Both play critical roles in achieving cost efficiency, improving customer satisfaction, and gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.

